
Demystifying BLE GATT: The Bedrock of Bluetooth Low Energy Communication
September 17, 2024

Central to BLE’s functionality is the BLE Generic Attribute Profile (BLE GATT), which serves as the protocol’s backbone, enabling efficient and structured data communication between devices. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of GATT, its components, and its role in BLE technology.
Understanding BLE GATT
BLE GATT is a protocol that operates on top of the Attribute Protocol (ATT) and is responsible for handling the exchange of information between BLE devices. It defines a standardized way of organizing data into readable formats, making it easier for devices to communicate with each other. GATT is particularly important in BLE because it allows devices to discover and understand the services and characteristics offered by other devices.
Services and Characteristics
At the heart of GATT are two key concepts: Services and Characteristics. A Service in GATT is a collection of data that represents a particular function of the device. For instance, a heart rate monitor might have a service that includes characteristics for heart rate measurement, body sensor location, and control points. Characteristics, on the other hand, are the smallest units of data within a service, representing specific values like the current heart rate or battery level.
Each characteristic has a unique identifier known as a Universally Unique Identifier (UUID), which allows devices to recognize and access them. Characteristics can be read, written, or both, depending on their properties, and they often include descriptors that provide additional information about the characteristic, such as its value range or unit of measurement.
The Role of UUIDs
UUIDs play a crucial role in GATT by providing a unique identity to services and characteristics. This ensures that data can be accurately identified and accessed, regardless of the device’s manufacturer. The Bluetooth SIG maintains a list of standardized UUIDs for commonly used services and characteristics, which promotes interoperability between different devices.
Data Transfer and Communication
Once a connection is established between two BLE devices, the GATT protocol facilitates the discovery of services and characteristics by the client device. This process involves the client device reading the attributes of the server device to identify the available services and characteristics.
After discovering the services and characteristics of interest, the client can read from or write to these characteristics to exchange data with the server. This exchange is managed by the ATT protocol, which provides the mechanisms for attribute access and data transfer.
Security and Privacy
GATT also addresses security and privacy concerns. It includes provisions for data encryption and authentication to ensure that data transfers are secure and that only authorized devices can access certain characteristics. This is particularly important for protecting sensitive data, such as health information from fitness trackers or personal identification data.
Applications and Use Cases
GATT is the foundation for a wide range of BLE applications, from health and fitness trackers to home automation and asset tracking. Its ability to define standardized services and characteristics makes it easy for developers to create interoperable applications that can work with a variety of BLE devices.
Conclusion
The Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) is a cornerstone of BLE technology, providing a structured and efficient way to organize and exchange data between devices. Its use of services, characteristics, and UUIDs, along with its support for security and privacy, makes it a powerful tool for developers looking to create innovative wireless applications. As BLE technology continues to evolve, GATT will remain a critical component, enabling the seamless connectivity that is the hallmark of modern wireless communication.
Leave a Reply
Related Products
You Might Like Also
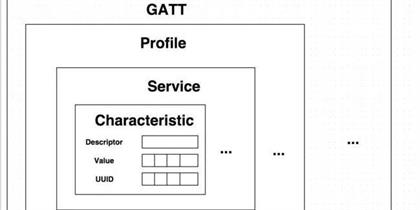
BLE Characteristics are the fundamental building blocks of GATT, representing the smallest unit of data that can be accessed, read, or written. They are the conduits through which devices exchange information, and their versatility is key to the dynamic nature of BLE technology. Read More

In the intricate world of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) communications, the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) plays a pivotal role in defining the structure and methods for data exchange. Central to this are the processes of Notifications and Indications, which are the primary means by which GATT servers update clients about changes in attribute values Read More
In the realm of wireless communication, Bluetooth advertising has carved out a niche for itself, becoming an indispensable technology for short-range connectivity. At the heart of Bluetooth functionality lies the advertising process, which is the cornerstone for device discoverability and connection establishment. This article delves into the intri Read More
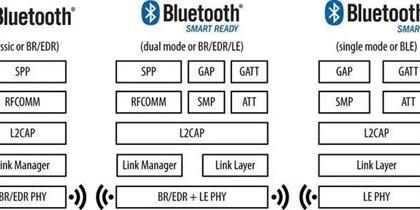
Bluetooth data structures are the foundational elements that govern how data is packaged, transmitted, and received within the Bluetooth ecosystem. These structures are designed to optimize the efficiency and reliability of wireless communication, ensuring that data is handled effectively across various devices and platforms. Read More
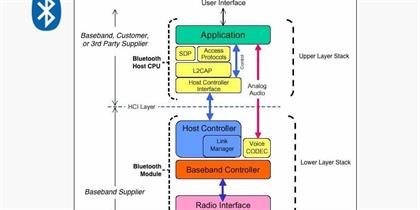
In the intricate world of wireless communication, Bluetooth Protocol Stack has established itself as a cornerstone technology, facilitating seamless connectivity between a plethora of devices. At the heart of this technology lies the Bluetooth protocol stack, a structured set of protocols that govern how devices communicate. One of the most critica Read More

In the intricate world of wireless communication, the Bluetooth Generic Access Profile (Bluetooth GAP) of Bluetooth technology stands as a cornerstone, enabling devices to connect, communicate, and collaborate seamlessly. This article delves into the essence of Bluetooth GAP, its role in establishing connections, and the myriad ways it enhances our Read More











