
The Dynamics of BLE GATT Notifications and Indications
September 18, 2024
 In the intricate world of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) communications, the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) plays a pivotal role in defining the structure and methods for data exchange. Central to this are the processes of Notifications and Indications, which are the primary means by which GATT servers update clients about changes in attribute values. This article delves into the subtleties and significance of these mechanisms, highlighting their roles in the efficient operation of BLE systems.
In the intricate world of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) communications, the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) plays a pivotal role in defining the structure and methods for data exchange. Central to this are the processes of Notifications and Indications, which are the primary means by which GATT servers update clients about changes in attribute values. This article delves into the subtleties and significance of these mechanisms, highlighting their roles in the efficient operation of BLE systems.
Understanding Notifications and Indications
At the core of BLE GATT operations are characteristics, which are the fundamental data elements that can be read or written. These characteristics can notify or indicate changes to connected clients. The distinction between these two lies in the nature of the communication and the level of reliability they offer.
- Notifications: A notification is a one-way communication from a GATT server to a client. It does not require an acknowledgment from the client. This makes notifications a faster method of data transmission but with less reliability. If a client does not read the data quickly enough, it may be overwritten by subsequent notifications.
- Indications: Indications, on the other hand, are also sent from a GATT server to a client, but they require an acknowledgment from the client. This confirmation ensures that the data has been received and processed, making indications a more reliable form of communication.
The Role of Client Characteristic Configuration Descriptor (CCCD)
Both notifications and indications are controlled by the CCCD, a special descriptor that determines how updates are sent from the GATT server to the client. The client must write to this descriptor to enable notifications or indications for a particular characteristic.
Data Reliability and Throughput
The choice between using notifications or indications often comes down to the required level of data reliability. Indications, while more reliable due to the acknowledgment requirement, can lead to lower throughput because the server must wait for a response before sending the next indication.
Notifications, not requiring acknowledgments, allow for a higher data throughput but at the risk of data loss if the client cannot read the data quickly enough. This makes notifications suitable for applications where data loss is acceptable and a higher data rate is preferred.
Implementation Considerations
Implementing notifications and indications involves several steps:
- Service and Characteristic Definition: The GATT server defines the services and characteristics, including which characteristics will support notifications or indications.
- CCCD Configuration: The client must configure the CCCD to enable the desired update mechanism. This configuration is crucial as it determines the client’s interest in receiving updates.
- Data Transmission: Once enabled, the GATT server can send notifications or indications. The client must be prepared to handle these updates, reading the data promptly to avoid loss in the case of notifications.
- Handling Responses: For indications, the client must send a response back to the server to acknowledge receipt. This response is vital for the server to know that it can proceed with subsequent updates.
Conclusion
Notifications and indications are powerful tools in the BLE GATT arsenal, offering developers a choice between speed and reliability based on the application’s needs. As BLE technology continues to evolve, the efficient use of these mechanisms will remain critical in ensuring that BLE devices operate effectively and meet user expectations. Whether it’s a fitness tracker updating a smartphone with the latest workout data or a smart home device signaling a change in state, the dynamics of BLE GATT notifications and indications underpin the seamless operation of these interactions.
Leave a Reply
Related Products
You Might Like Also
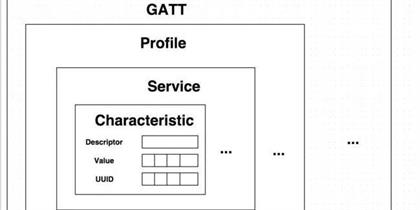
BLE Characteristics are the fundamental building blocks of GATT, representing the smallest unit of data that can be accessed, read, or written. They are the conduits through which devices exchange information, and their versatility is key to the dynamic nature of BLE technology. Read More
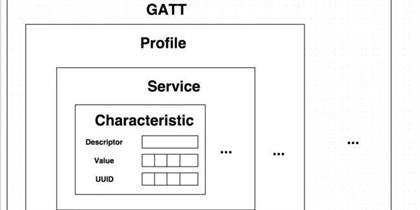
Central to BLE’s functionality is the BLE Generic Attribute Profile (BLE GATT), which serves as the protocol’s backbone, enabling efficient and structured data communication between devices. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of GATT, its components, and its role in BLE technology. Read More
In the realm of wireless communication, Bluetooth advertising has carved out a niche for itself, becoming an indispensable technology for short-range connectivity. At the heart of Bluetooth functionality lies the advertising process, which is the cornerstone for device discoverability and connection establishment. This article delves into the intri Read More
Bluetooth data structures are the foundational elements that govern how data is packaged, transmitted, and received within the Bluetooth ecosystem. These structures are designed to optimize the efficiency and reliability of wireless communication, ensuring that data is handled effectively across various devices and platforms. Read More
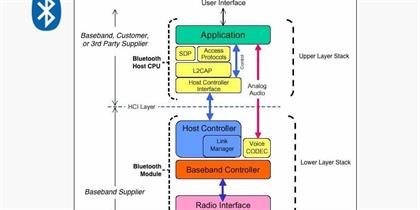
In the intricate world of wireless communication, Bluetooth Protocol Stack has established itself as a cornerstone technology, facilitating seamless connectivity between a plethora of devices. At the heart of this technology lies the Bluetooth protocol stack, a structured set of protocols that govern how devices communicate. One of the most critica Read More

In the intricate world of wireless communication, the Bluetooth Generic Access Profile (Bluetooth GAP) of Bluetooth technology stands as a cornerstone, enabling devices to connect, communicate, and collaborate seamlessly. This article delves into the essence of Bluetooth GAP, its role in establishing connections, and the myriad ways it enhances our Read More











