
Unveiling the Mysteries of Bluetooth Advertising and Initiating Connections
September 16, 2024
 In the realm of wireless communication, Bluetooth advertising has carved out a niche for itself, becoming an indispensable technology for short-range connectivity. At the heart of Bluetooth functionality lies the advertising process, which is the cornerstone for device discoverability and connection establishment. This article delves into the intricacies of Bluetooth advertising and the initiation of connections, shedding light on how these mechanisms power the dynamic world of Bluetooth-enabled devices.
In the realm of wireless communication, Bluetooth advertising has carved out a niche for itself, becoming an indispensable technology for short-range connectivity. At the heart of Bluetooth functionality lies the advertising process, which is the cornerstone for device discoverability and connection establishment. This article delves into the intricacies of Bluetooth advertising and the initiation of connections, shedding light on how these mechanisms power the dynamic world of Bluetooth-enabled devices.
The Essence of Bluetooth Advertising
Bluetooth advertising is a broadcast mechanism that allows devices to make their presence known to the world. It is akin to a town crier in medieval times, proclaiming news and events to the populace. In the Bluetooth ecosystem, an advertising packet is the town crier’s scroll, containing essential information about the device and its services.
Advertising packets are transmitted on specific frequencies within the 2.4 GHz ISM band, which is divided into 40 channels for Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) devices. Three of these channels are designated as primary advertising channels, while the remaining 37 serve dual purposes—acting as secondary advertising channels and carrying data during established connections.
The Advertising Process
The advertising process begins with the device entering the advertising state. In this state, the device becomes discoverable, sending out advertising packets at regular intervals known as the advertising interval. These intervals can be programmed to vary, allowing for different levels of discoverability and power consumption.
Each advertising packet contains a payload, which is a collection of information that can include the device’s Bluetooth address, its name, the type of service it provides, and more. This payload is crucial for attracting the attention of nearby devices that might be interested in establishing a connection.
The Role of the Advertising Interval
The advertising interval is a key parameter that determines how frequently a device broadcasts its advertising packets. It is a balance between being discoverable and conserving power. A shorter interval means the device is more frequently discoverable but consumes more power, while a longer interval conserves power at the cost of reduced discoverability.
Devices like smartphones and tablets, which are typically power-rich compared to sensors and wearables, can afford shorter intervals. On the other hand, devices designed for low-power operation, such as fitness trackers and environmental sensors, might opt for longer intervals to extend battery life.
Initiating a Connection
Once a device has received an advertising packet and is interested in establishing a connection, it enters the initiating state. In this state, the device sends out connection requests on the primary advertising channels, hoping for a response from the advertiser.
The connection request is a specialized packet that includes the advertiser’s address and a series of parameters that define the characteristics of the desired connection, such as its interval, duration, and latency.
The Dance of Connection Establishment
Connection establishment in Bluetooth is a delicate dance between two devices. The initiator sends out a connection request, and if the advertiser is receptive and the parameters align, a connection is established. This process involves a series of exchanges, including link layer control packets that negotiate the final connection parameters.
Once the connection is established, the devices can begin to exchange data packets, moving from the advertising and initiating states to the connected state. This state is characterized by a continuous exchange of data, with the devices following a schedule that ensures timely and reliable communication.
Challenges and Considerations
The process of advertising and initiating connections is not without its challenges. Interference from other wireless devices, the varying quality of radio frequency environments, and the need to balance power consumption with performance are all factors that must be carefully managed.
Bluetooth devices must also contend with the limitations of the shared 2.4 GHz band. This band is a crowded airspace, with other technologies such as Wi-Fi, microwave ovens, and cordless phones all vying for a slice of the spectrum. Bluetooth devices use sophisticated frequency hopping algorithms to minimize the impact of this interference.
Leave a Reply
Related Products
You Might Like Also

In the intricate world of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) communications, the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) plays a pivotal role in defining the structure and methods for data exchange. Central to this are the processes of Notifications and Indications, which are the primary means by which GATT servers update clients about changes in attribute values Read More
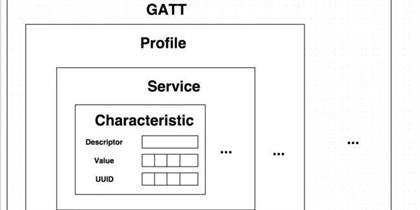
Central to BLE’s functionality is the BLE Generic Attribute Profile (BLE GATT), which serves as the protocol’s backbone, enabling efficient and structured data communication between devices. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of GATT, its components, and its role in BLE technology. Read More
Bluetooth data structures are the foundational elements that govern how data is packaged, transmitted, and received within the Bluetooth ecosystem. These structures are designed to optimize the efficiency and reliability of wireless communication, ensuring that data is handled effectively across various devices and platforms. Read More
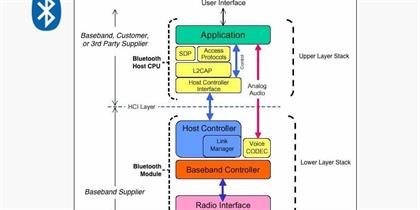
In the intricate world of wireless communication, Bluetooth Protocol Stack has established itself as a cornerstone technology, facilitating seamless connectivity between a plethora of devices. At the heart of this technology lies the Bluetooth protocol stack, a structured set of protocols that govern how devices communicate. One of the most critica Read More

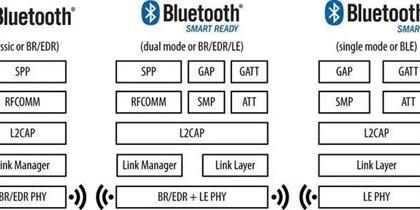
In the intricate world of wireless communication, the Bluetooth Generic Access Profile (Bluetooth GAP) of Bluetooth technology stands as a cornerstone, enabling devices to connect, communicate, and collaborate seamlessly. This article delves into the essence of Bluetooth GAP, its role in establishing connections, and the myriad ways it enhances our Read More

The Data Transport Architecture in BLE is designed to accommodate the needs of low-power, low-data rate applications while maintaining high reliability. It operates on a connection-oriented basis, where devices establish a connection before data exchange commences. This architecture is composed of several key elements, including the Logical Link Co Read More











