
Exploring the Bluetooth GAP: The Foundation of Wireless Connectivity
September 13, 2024
 In the intricate world of wireless communication, the Bluetooth Generic Access Profile (Bluetooth GAP) of Bluetooth technology stands as a cornerstone, enabling devices to connect, communicate, and collaborate seamlessly. This article delves into the essence of Bluetooth GAP, its role in establishing connections, and the myriad ways it enhances our digital interactions.
In the intricate world of wireless communication, the Bluetooth Generic Access Profile (Bluetooth GAP) of Bluetooth technology stands as a cornerstone, enabling devices to connect, communicate, and collaborate seamlessly. This article delves into the essence of Bluetooth GAP, its role in establishing connections, and the myriad ways it enhances our digital interactions.
Understanding Bluetooth GAP
Bluetooth GAP is a fundamental part of the Bluetooth Core Specification, which defines how devices discover each other, establish connections, and exchange data. GAP is responsible for device discovery, link management, and security, providing a standardized approach to Bluetooth communication.
The Role of GAP in Bluetooth Communication
GAP plays a pivotal role in the Bluetooth communication process. It manages the initial stages of device interaction, including:
- Device Discovery: GAP allows devices to broadcast their presence, enabling other devices to discover them. This process is known as advertising.
- Connection Establishment: Once a device is discovered, GAP facilitates the creation of a connection between devices, ensuring that they can communicate effectively.
- Link Management: GAP oversees the maintenance of the Bluetooth link, handling tasks such as connection parameter updates and link supervision.
- Security: GAP is integral to the security of Bluetooth connections, managing authentication and encryption to protect data integrity and privacy.
Key Components of Bluetooth GAP
The Bluetooth GAP comprises several key components that enable efficient and secure communication:
- GAP Roles: Devices can operate in various roles, such as the Central role (initiating connections) or the Peripheral role (accepting connections).
- GAP Procedures: These are the processes that GAP uses to manage device interactions, including procedures for device discovery, connection establishment, and link management.
- GAP Attributes: Attributes define the characteristics of a Bluetooth device, such as its name, class of device, and appearance.
Applications of Bluetooth GAP
Bluetooth GAP is the backbone of many wireless applications, including:
- Smart Home Systems: GAP enables devices like smart speakers, thermostats, and lighting systems to connect and work together, creating a cohesive smart home ecosystem.
- Health and Fitness: Wearable devices use GAP for data synchronization, allowing users to track their health and fitness metrics seamlessly.
- Beacons and Proximity Services: Retailers and service providers use GAP to deliver personalized experiences based on a user’s proximity to a beacon.
- Industrial Automation: GAP facilitates the connection of sensors, controllers, and machines, streamlining industrial processes and enhancing efficiency.
The Future of Bluetooth GAP
As technology advances, the capabilities of Bluetooth GAP are expected to expand. With the ongoing development of Bluetooth standards, we can anticipate improvements in connection speed, range, and security, further enhancing the performance of Bluetooth-enabled devices.
Privacy and Security in Bluetooth GAP
Privacy and security are paramount in Bluetooth communication. GAP ensures that devices can securely connect, with features such as secure pairing and data encryption to protect against unauthorized access and eavesdropping.
Conclusion
Bluetooth GAP is the unsung hero of wireless connectivity, quietly working behind the scenes to ensure that our devices can connect and communicate effectively. As we continue to rely on Bluetooth technology for various aspects of our lives, the role of GAP will remain crucial in shaping the future of wireless communication.
Leave a Reply
Related Products
You Might Like Also

In the intricate world of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) communications, the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) plays a pivotal role in defining the structure and methods for data exchange. Central to this are the processes of Notifications and Indications, which are the primary means by which GATT servers update clients about changes in attribute values Read More
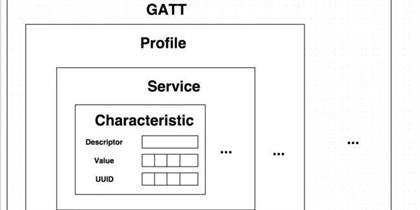
Central to BLE’s functionality is the BLE Generic Attribute Profile (BLE GATT), which serves as the protocol’s backbone, enabling efficient and structured data communication between devices. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of GATT, its components, and its role in BLE technology. Read More
In the realm of wireless communication, Bluetooth advertising has carved out a niche for itself, becoming an indispensable technology for short-range connectivity. At the heart of Bluetooth functionality lies the advertising process, which is the cornerstone for device discoverability and connection establishment. This article delves into the intri Read More
Bluetooth data structures are the foundational elements that govern how data is packaged, transmitted, and received within the Bluetooth ecosystem. These structures are designed to optimize the efficiency and reliability of wireless communication, ensuring that data is handled effectively across various devices and platforms. Read More
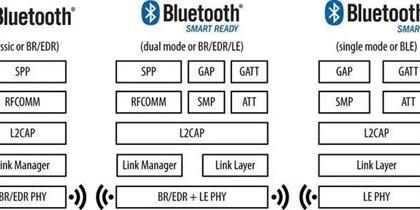
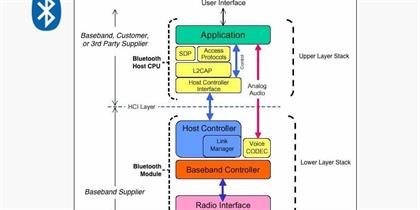
In the intricate world of wireless communication, Bluetooth Protocol Stack has established itself as a cornerstone technology, facilitating seamless connectivity between a plethora of devices. At the heart of this technology lies the Bluetooth protocol stack, a structured set of protocols that govern how devices communicate. One of the most critica Read More

The Data Transport Architecture in BLE is designed to accommodate the needs of low-power, low-data rate applications while maintaining high reliability. It operates on a connection-oriented basis, where devices establish a connection before data exchange commences. This architecture is composed of several key elements, including the Logical Link Co Read More











