
Demystifying Bluetooth Data Structures: A Deep Dive into the Core of Wireless Communication
September 15, 2024
 In the intricate world of wireless communication, Bluetooth technology has become an essential fabric of our connected lives. At the heart of this technology lies a complex yet efficient system of data structures that enable devices to communicate seamlessly. This article aims to demystify these data structures, shedding light on the core mechanisms that power Bluetooth devices.
In the intricate world of wireless communication, Bluetooth technology has become an essential fabric of our connected lives. At the heart of this technology lies a complex yet efficient system of data structures that enable devices to communicate seamlessly. This article aims to demystify these data structures, shedding light on the core mechanisms that power Bluetooth devices.
Understanding Bluetooth Data Structures
Bluetooth data structures are the foundational elements that govern how data is packaged, transmitted, and received within the Bluetooth ecosystem. These structures are designed to optimize the efficiency and reliability of wireless communication, ensuring that data is handled effectively across various devices and platforms.
The Role of Data Structures in Bluetooth Communication
Data structures play a pivotal role in Bluetooth communication, serving several key functions:
- Data Packaging: They define how data is organized and packaged for transmission, ensuring that the data is sent in a structured and recognizable format.
- Error Detection and Correction: Data structures often include mechanisms for error detection and correction, which are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the data during transmission.
- Synchronization: They facilitate synchronization between devices, ensuring that data is transmitted and received in a coordinated manner.
- Efficiency: By optimizing the way data is handled, data structures contribute to the overall efficiency of Bluetooth communication, reducing latency and improving performance.
Key Bluetooth Data Structures
Several key data structures are integral to the functioning of Bluetooth technology:
- HCI (Host Controller Interface) Commands and Events: These structures define the commands sent from the host to the controller and the events reported by the controller to the host.
- L2CAP (Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol) PDUs: L2CAP data structures manage the segmentation and reassembly of data packets, ensuring efficient data transfer between devices.
- GATT (Generic Attribute Profile) Services and Characteristics: GATT structures define the services and characteristics that are exposed by Bluetooth devices, allowing for the exchange of data and commands.
- SDP (Service Discovery Protocol) Records: SDP structures facilitate the discovery of services and their attributes, enabling devices to identify and connect to available services.
Applications of Bluetooth Data Structures
Bluetooth data structures are applied across a wide range of applications, including:
- Device Pairing and Bonding: Data structures ensure that devices can securely pair and bond, establishing a trusted connection for data exchange.
- Data Transfer: They enable the efficient transfer of data between devices, whether it’s for file sharing, streaming media, or real-time communication.
- Service Discovery: Data structures allow devices to discover available services and characteristics, streamlining the process of connecting to and interacting with Bluetooth devices.
- Device Management: They provide the framework for managing device connections, handling multiple connections, and ensuring that devices can be controlled and monitored effectively.
The Future of Bluetooth Data Structures
As Bluetooth technology continues to evolve, the data structures that underpin it are also expected to advance. Future developments may include:
- Enhanced Security: Data structures could incorporate more robust security features to protect against vulnerabilities and threats.
- Improved Efficiency: With the growing demand for faster data transfer, data structures may be optimized for higher throughput and reduced latency.
- Scalability: As the number of connected devices increases, data structures will need to scale to accommodate a larger number of devices and connections.
Conclusion
Bluetooth data structures are the unsung heroes of wireless communication, quietly ensuring that our devices can communicate effectively and efficiently. As we continue to rely on Bluetooth technology for various aspects of our daily lives, the importance of these data structures cannot be overstated. As technology progresses, the evolution of Bluetooth data structures will play a crucial role in shaping the future of wireless communication.
Leave a Reply
Related Products
You Might Like Also

In the intricate world of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) communications, the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) plays a pivotal role in defining the structure and methods for data exchange. Central to this are the processes of Notifications and Indications, which are the primary means by which GATT servers update clients about changes in attribute values Read More
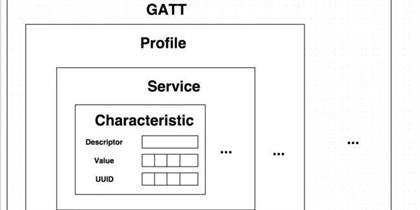
Central to BLE’s functionality is the BLE Generic Attribute Profile (BLE GATT), which serves as the protocol’s backbone, enabling efficient and structured data communication between devices. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of GATT, its components, and its role in BLE technology. Read More
In the realm of wireless communication, Bluetooth advertising has carved out a niche for itself, becoming an indispensable technology for short-range connectivity. At the heart of Bluetooth functionality lies the advertising process, which is the cornerstone for device discoverability and connection establishment. This article delves into the intri Read More
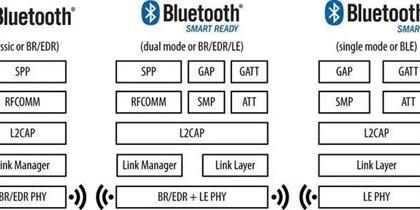
In the intricate world of wireless communication, Bluetooth Protocol Stack has established itself as a cornerstone technology, facilitating seamless connectivity between a plethora of devices. At the heart of this technology lies the Bluetooth protocol stack, a structured set of protocols that govern how devices communicate. One of the most critica Read More

In the intricate world of wireless communication, the Bluetooth Generic Access Profile (Bluetooth GAP) of Bluetooth technology stands as a cornerstone, enabling devices to connect, communicate, and collaborate seamlessly. This article delves into the essence of Bluetooth GAP, its role in establishing connections, and the myriad ways it enhances our Read More

The Data Transport Architecture in BLE is designed to accommodate the needs of low-power, low-data rate applications while maintaining high reliability. It operates on a connection-oriented basis, where devices establish a connection before data exchange commences. This architecture is composed of several key elements, including the Logical Link Co Read More











