
BLE Beacons: The Pulse of Hospital Asset Tracking
September 07, 2024
 In the corridors of healthcare, where every second counts and every device is vital, BLE Beacons (Bluetooth Low Energy Beacons) have become the pulse that drives hospital asset tracking. These beacons are not just pieces of technology; they are the lifelines that ensure medical equipment is always where it needs to be, when it needs to be there.
In the corridors of healthcare, where every second counts and every device is vital, BLE Beacons (Bluetooth Low Energy Beacons) have become the pulse that drives hospital asset tracking. These beacons are not just pieces of technology; they are the lifelines that ensure medical equipment is always where it needs to be, when it needs to be there.
The Silent Guardians: BLE Beacons in Healthcare
BLE Beacons are small, unobtrusive devices that use Bluetooth technology to communicate with nearby devices. In hospitals, they serve as the silent guardians of assets, providing real-time tracking and management that can enhance efficiency and patient care.
The Role of BLE Beacons in Hospital Asset Tracking
Hospitals are complex environments with a multitude of assets, from medical equipment to patient records. BLE Beacons play a crucial role in tracking these assets, ensuring they are available when needed and accounted for at all times.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of BLE Beacons in hospitals is the enhancement of operational efficiency. By tracking the location of equipment, hospitals can reduce the time spent searching for devices, ensuring that medical staff can focus on patient care rather than equipment management.
Improving Patient Safety
Patient safety is a top priority in healthcare, and BLE Beacons can contribute to this by ensuring that critical equipment is always available. For example, beacons can track the location of defibrillators, ensuring that they can be quickly located in emergency situations.
Optimizing Maintenance and Inventory Management
Regular maintenance is essential for medical equipment to function properly. BLE Beacons can monitor the usage of equipment, triggering alerts for maintenance when necessary. This proactive approach can extend the life of assets and reduce the risk of equipment failure.
Applications of BLE Beacons in Hospital Settings
BLE Beacons have a wide range of applications in hospital settings:
- Equipment Tracking: Track the location of medical equipment, from portable ultrasound machines to wheelchairs, ensuring they are available when needed.
- Pharmacy Management: Monitor the movement and storage conditions of pharmaceuticals, ensuring that medications are always stored correctly and accounted for.
- Patient Flow: Improve patient flow by tracking the location of patients and staff, optimizing the allocation of resources and reducing wait times.
- Emergency Response: Enhance emergency response times by tracking the location of emergency equipment and personnel, ensuring a rapid response to critical situations.
The Future of BLE Beacons in Healthcare
As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of BLE Beacons are expected to grow. With advancements in AI and machine learning, beacons could offer predictive maintenance insights, automated equipment dispatching, and even real-time patient monitoring.
Privacy and Data Security
Privacy is a significant concern in healthcare, where patient data is sensitive. Hospitals must ensure that the use of BLE Beacons complies with data protection regulations and that all data is handled securely and transparently.
Conclusion
BLE Beacons are the pulse of hospital asset tracking, offering a beacon of hope for a more efficient, safe, and intelligent healthcare system. As the industry continues to embrace smart technology, BLE Beacons will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of healthcare operations.
Leave a Reply
Related Products
You Might Like Also
In the realm of wireless communication, Bluetooth advertising has carved out a niche for itself, becoming an indispensable technology for short-range connectivity. At the heart of Bluetooth functionality lies the advertising process, which is the cornerstone for device discoverability and connection establishment. This article delves into the intri Read More
Bluetooth data structures are the foundational elements that govern how data is packaged, transmitted, and received within the Bluetooth ecosystem. These structures are designed to optimize the efficiency and reliability of wireless communication, ensuring that data is handled effectively across various devices and platforms. Read More
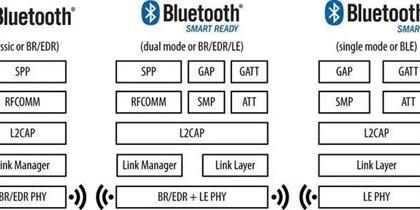
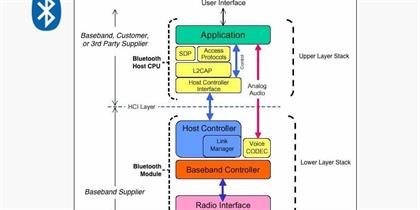
In the intricate world of wireless communication, Bluetooth Protocol Stack has established itself as a cornerstone technology, facilitating seamless connectivity between a plethora of devices. At the heart of this technology lies the Bluetooth protocol stack, a structured set of protocols that govern how devices communicate. One of the most critica Read More

In the intricate world of wireless communication, the Bluetooth Generic Access Profile (Bluetooth GAP) of Bluetooth technology stands as a cornerstone, enabling devices to connect, communicate, and collaborate seamlessly. This article delves into the essence of Bluetooth GAP, its role in establishing connections, and the myriad ways it enhances our Read More

The Data Transport Architecture in BLE is designed to accommodate the needs of low-power, low-data rate applications while maintaining high reliability. It operates on a connection-oriented basis, where devices establish a connection before data exchange commences. This architecture is composed of several key elements, including the Logical Link Co Read More

The Physical Layer is the foundation of any wireless communication protocol, including Bluetooth LE. It defines the basic parameters for the transmission of raw data bits over the air. In the context of BLE, the PHY is responsible for modulating the data onto a carrier signal, transmitting it through the antenna, and then demodulating the received Read More











